 Screen space is a precious resource on mobile. To meet the challenge of small screen space while still making navigation accessible, designers often rely on hiding navigation behind the hamburger icon, a prime example of hidden navigation. In this article, we’ll see why hidden navigation creates bad UX and what alternatives are available for designers.
Screen space is a precious resource on mobile. To meet the challenge of small screen space while still making navigation accessible, designers often rely on hiding navigation behind the hamburger icon, a prime example of hidden navigation. In this article, we’ll see why hidden navigation creates bad UX and what alternatives are available for designers.
Why the Hamburger Menu Is Bad For UX
On mobile, visible navigation is used 1.5x more than hamburger
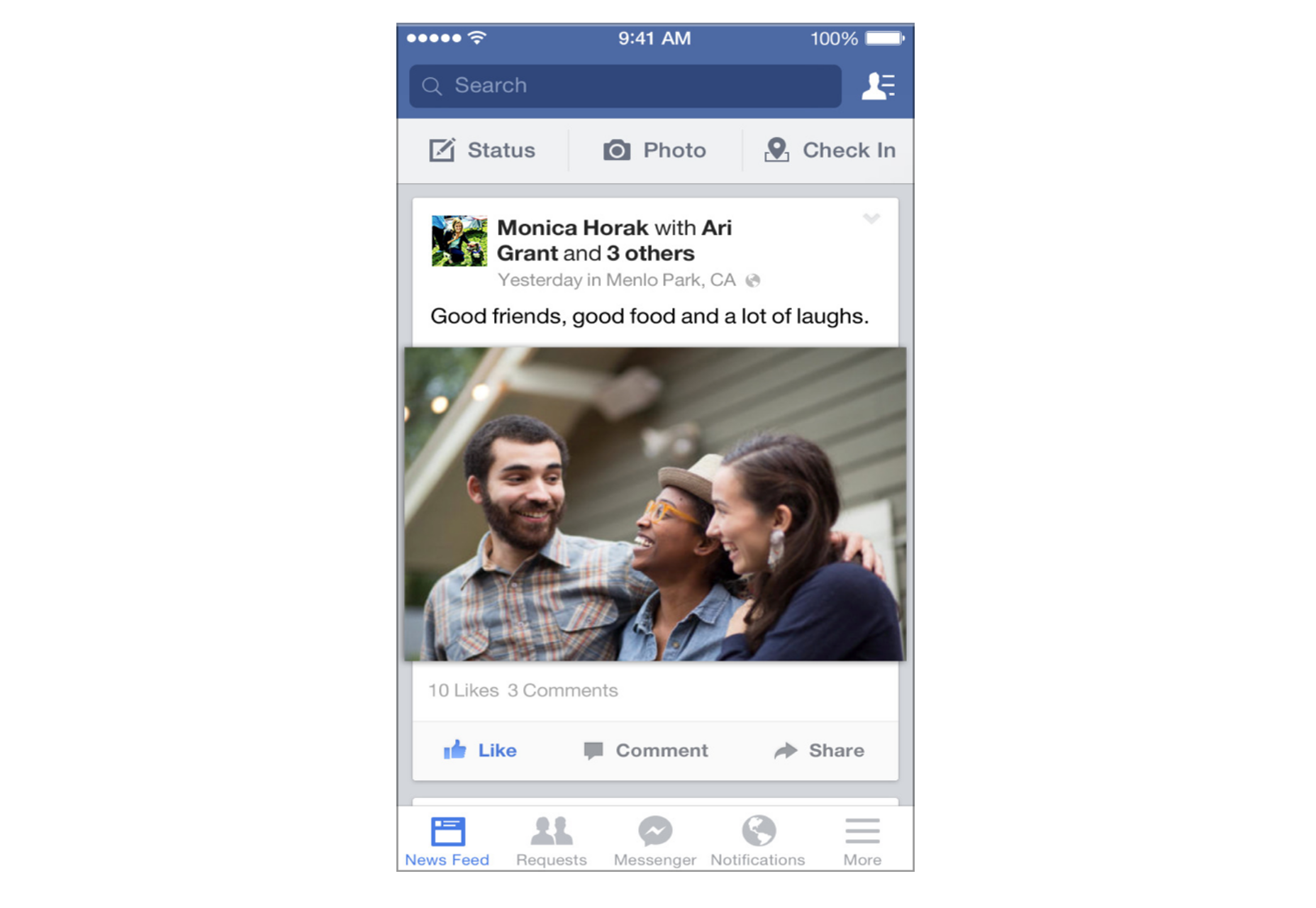
If you’re working on digital products, you’ve probably already read dozens of articles describing how the hamburger menu on mobile hurts UX metrics. The main downside is its low discoverability, and this is backed up by actual numbers. In qualitative studies, NNGroup found that hidden navigation is less discoverable than visible or partially visible navigation. This means that when navigation is hidden, users are less likely to use navigation. Hamburger menus drive engagement down, slow down exploration and confuse people.
So What Should We Use Instead?
While there is no hard-and-fast rule for mobile apps and websites, a general recommendation is to use either visible—the main navigation options are shown in a visible navigation bar—or combo navigation, where some of the main navigation options are visible and some are hidden under an interactive element.
1. Tab Bar
If you have a limited number of top-level destinations in your website or app, a tabbed navigation might be the solution. When a menu is visible at the top or bottom, it’s basically advertising that a navigation is there and people are able to see the navigation options right from the start.
Tabs seem to be the simplest navigation pattern. However, a few things should be considered when designing this type of navigation:
- Tab bar allows 5 or fewer navigation options to display.
- One of the options should always be active and should be visually highlighted by, for example, using a contrasting color.
- The first tab has to be the home page and the order of the tabs should relate to their priority or logical order in the user flow.
- It’s better to use icons together with labels for each navigation option. Icons without labels work only for common actions, like a magnifying glass icon for search, and for interfaces that the users use frequently (e.g. Instagram).
Tip: In order to save screen space, the navigation bar could be hidden/revealed on downward and upward scrolling.
2. Tab Bar With “More” Option
When you have more than 5 top-level destinations, a practical solution might be to show the 4 prioritized sections and have a 5th element as a list of remaining options.
The design principles for this solution are basically the same as for Tab bar. There’s just one exception: the last element is the ‘more’ item.
The ‘more’ item can work as a dropdown menu or even link to a separate navigation page with the remaining sections. From the first glance this solution isn’t much better than the hamburger menu, since it also hides content and its label doesn’t say too much about what’s hidden behind it. If you correctly prioritize navigation options, however, a majority of your users will have 4 or 5 visible top-priority navigation options on the screen all the time so the navigation experience for them will be improved.
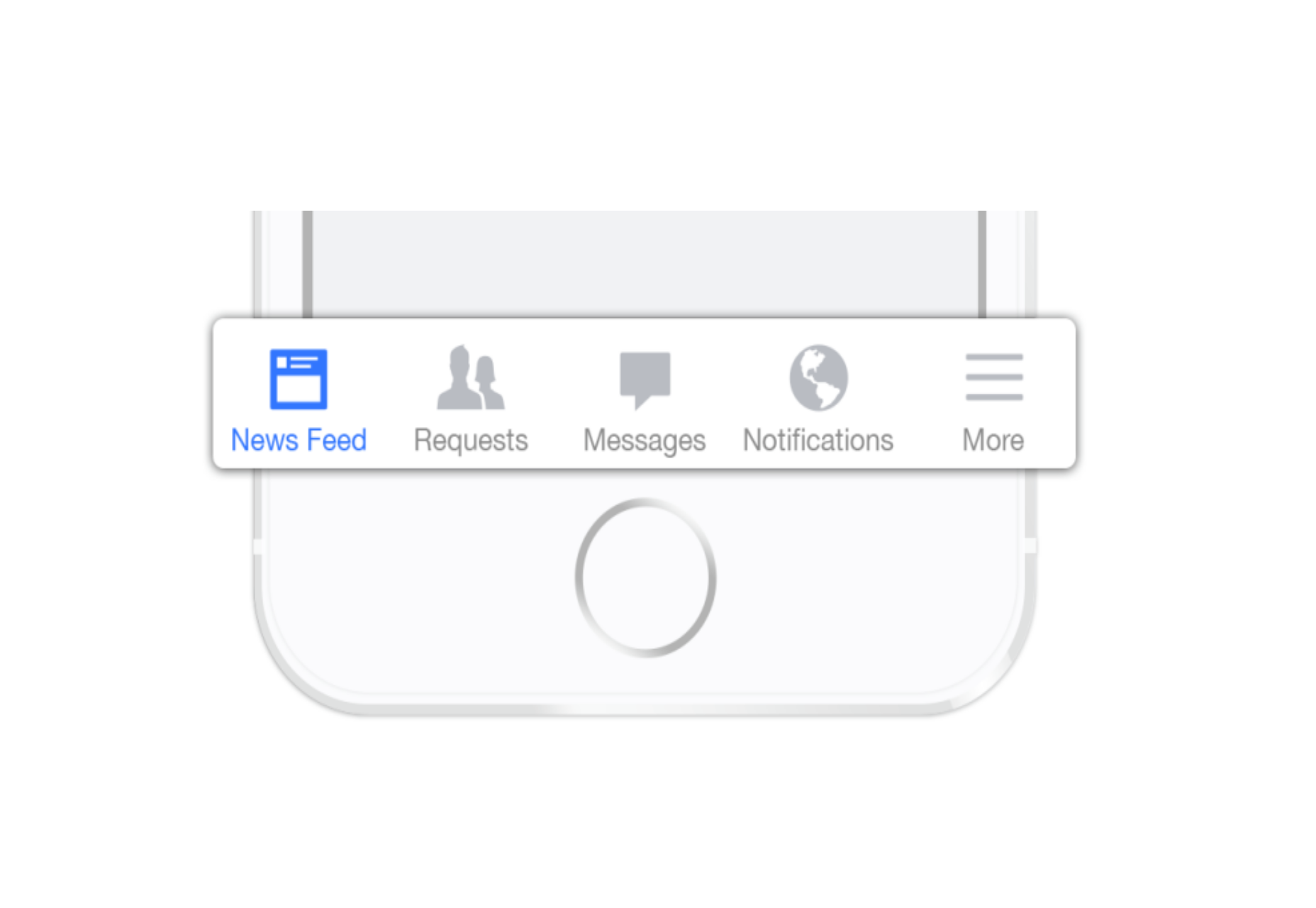
3. Progressively Collapsing Menu
Progressively collapsing menu, also known as the “Priority+” pattern, is a menu that adapts to the screen width. It shows as much of the navigation as possible and puts everything else under a “more” button. Basically, this pattern is a sophisticated version of the ‘Tab bar + more’ navigation where the number of navigation options hidden behind the “more” menu depends on the available screen space. The flexibility of this solution provides a better user experience than a ‘static’ ‘Tab bar + more’.
Image Credit: Brad Frost
4. Scrollable Navigation
Similar to the previous two patterns, this is another approach for longer lists. If you have a number of navigation options without a big distinction in priorities, for example music genres, you can list all the items in a scrollable view. By making the list scrollable you allow users to move from side-to-side.
The downside of this solution is that still only the top few items are visible without scrolling and all the remaining ones are out of the sight. This is, however, an acceptable solution when the users are expected to explore the content, for example news categories, music categories or in an online store.
5. Full-Screen Navigation
While with other patterns mentioned in this article, the struggle is to minimize the space that the navigation systems take up, the full-screen pattern takes the exact opposite approach. This approach usually devotes the home page exclusively to navigation. Users incrementally tap or swipe to reveal additional menu options as they scroll up and down.
This pattern works well in task-based and direction-based websites and apps, especially when users tend to limit themselves to only one branch of the navigation hierarchy during a single session. Funnelling users from broad overview pages to detail pages helps them to home in on what they’re looking for and to focus on content within an individual section.
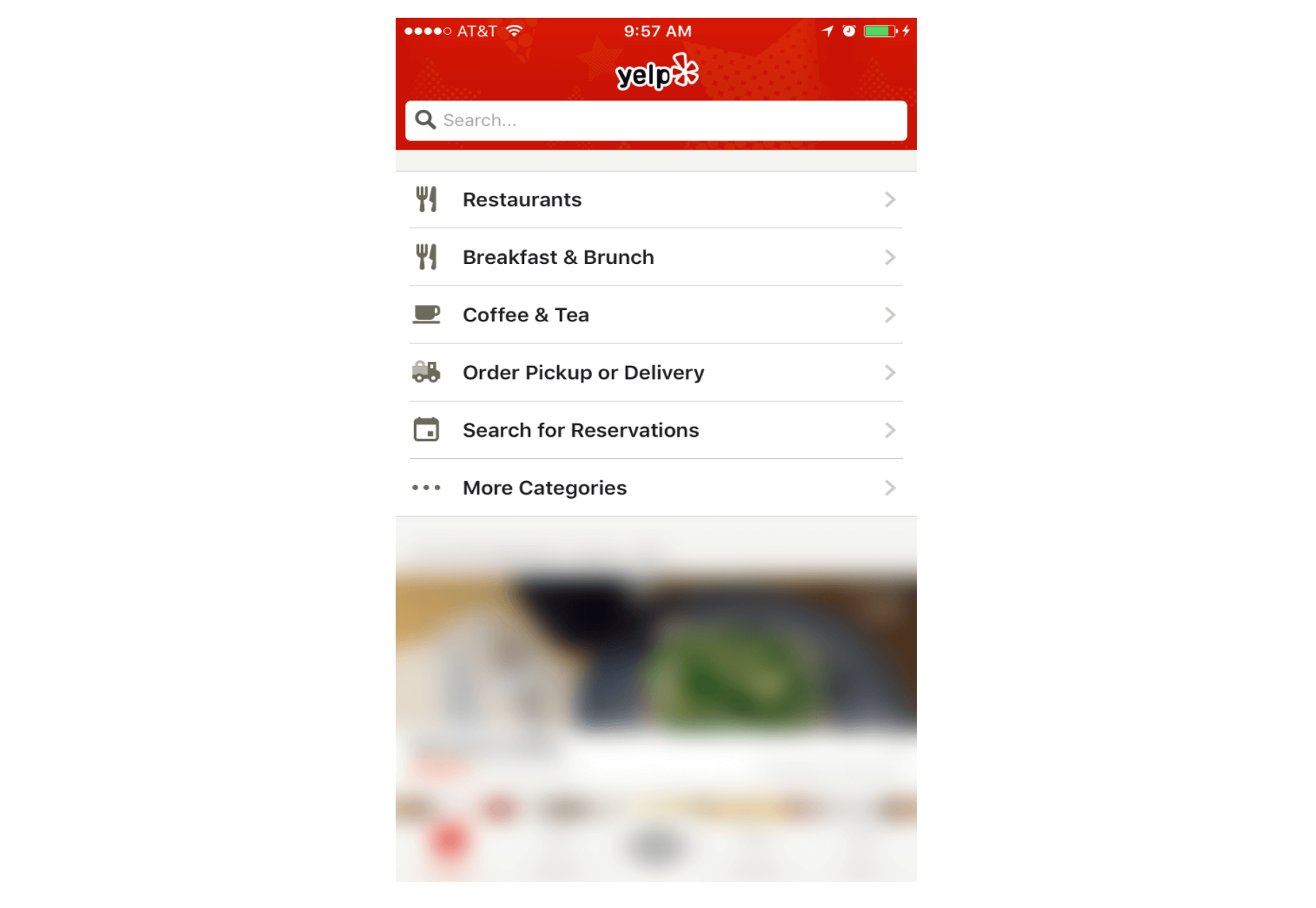
Full-screen navigation in Yelp
Using full-screen navigation, designers can organize large chunks of information in a coherent manner and reveal information without overwhelming the user. Once the user makes their decision about where to go, then you can dedicate the entire screen space to content.
Conclusion
With navigation patterns for mobile, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution; it always depends on your product, on your users, and on the context. However, the foundation of every well-designed navigation is information architecture: clear structure, priorities, and labels based on your users’ needs. Helping users navigate should be a top priority for every app designer. Both first-time and returning users should be able to figure out how to move through your app with ease.
| 850 Quality, Customizable Infographics Templates – only $19! |
from Webdesigner Depot https://www.webdesignerdepot.com/2017/08/5-smart-alternatives-to-the-hamburger-menu/


No comments:
Post a Comment